1- Kidney Stones
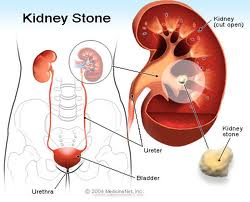
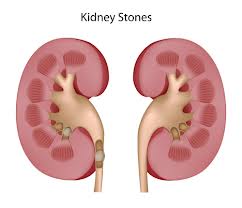
Kidney Stones (renal lithiasis) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The stones are made of mineral and acid salts. Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together.
Passing kidney stones can be quite painful, but the stones usually cause no permanent damage. Depending on your situation, you may need nothing more than to take pain medication and drink lots of water to pass a kidney stone. In other instances, surgery may be needed. Your doctor may recommend preventive treatment to reduce your risk of recurrent kidney stones if you're at increased risk of developing them again.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
A kidney stone may not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureter — the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. At that point, these signs and symptoms may occur:1. Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs.
2. Pain that spreads to the lower abdomen and groin.
3. Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity.
4. Pain on urination.
5. Pink, red or brown urine.
6. Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
7. Nausea and vomiting.
8. Persistent urge to urinate.
9. Urinating more often than usual.
10. Fever and chills if an infection is present.
Pain caused by a kidney stone may change — for instance, shifting to a different location or increasing in intensity — as the stone moves through your urinary tract.
 When to see a doctor
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs and symptoms that worry you.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
• Pain so severe that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position.
• Pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
• Pain accompanied by fever and chills.
• Blood in your urine.
• Difficulty passing urine.
Causes
Kidney stones often have no definite, single cause, although several factors may increase your risk.Kidney stones form when your urine contains more crystal-forming substances — such as calcium, oxalate and uric acid — than the fluid in your urine can dilute. At the same time, your urine may lack substances that keep crystals from sticking together, creating an ideal environment for kidney stones to form.
Types of kidney stones
Knowing the type of kidney stone helps determine the cause and may give clues on how to reduce your risk of getting more kidney stones. Types of kidney stones include:• Calcium stones: Most kidney stones are calcium stones, usually in the form of calcium oxalate. Oxalate is a naturally occurring substance found in food. Some fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and chocolate, have high oxalate levels. Your liver also produces oxalate. Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, intestinal bypass surgery and several metabolic disorders can increase the concentration of calcium or oxalate in urine. Calcium stones may also occur in the form of calcium phosphate.
• Struvite stones: Struvite stones form in response to an infection, such as a urinary tract infection. These stones can grow quickly and become quite large, sometimes with few symptoms or little warning.
• Uric acid stones: Uric acid stones can form in people who don't drink enough fluids or who lose too much fluid, those who eat a high-protein diet, and those who have gout. Certain genetic factors also may increase your risk of uric acid stones.
• Cystine stones: These stones form in people with a hereditary disorder that causes the kidneys to excrete too much of certain amino acids (cystinuria).
• Other stones: Other, rarer types of kidney stones can occur.
Risk factors for Kidney Stones
Factors that increase your risk of developing kidney stones include:• Family or personal history. If someone in your family has kidney stones, you're more likely to develop stones, too. And if you've already had one or more kidney stones, you're at increased risk of developing another.
• Being an adult. Kidney stones are most common in adults age 40 and older, though kidney stones may occur at any age.
• Being a man. Men are more likely to develop kidney stones, although an increasing number of women are developing kidney stones.
• Dehydration. Not drinking enough water each day can increase your risk of kidney stones. People who live in warm climates and those who sweat a lot may be at higher risk than others.
• Certain diets. Eating a diet that's high in protein, sodium and sugar may increase your risk of some types of kidney stones. This is especially true with a high-sodium diet. Too much sodium in your diet increases the amount of calcium your kidneys must filter and significantly increases your risk of kidney stones.
• Being obese. High body mass index (BMI), large waist size and weight gain have been linked to an increased risk of kidney stones.
• Digestive diseases and surgery. Gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic diarrhea can cause changes in the digestive process that affect your absorption of calcium and water, increasing the levels of stone-forming substances in your urine.
• Other medical conditions. Diseases and conditions that may increase your risk of kidney stones include renal tubular acidosis, cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism, certain medications and some urinary tract infections.
Tests and diagnosis
If your doctor suspects you have a kidney stone, you may have diagnostic tests and procedures, such as:• Blood tests. Blood tests may reveal too much calcium or uric acid in your blood. Blood test results help monitor the health of your kidneys and may lead your doctor to check for other medical conditions.
• Urine tests. Tests of your urine, such as the 24-hour urine collection, may show that you're excreting too many stone-forming minerals or too few stone-preventing substances.
• Imaging tests.. Imaging tests may show kidney stones in your urinary tract. Options range from simple abdominal X-rays, which can miss small kidney stones, to high-speed computerized tomography (CT) that may reveal even tiny stones. Other imaging options include an ultrasound, a noninvasive test, and intravenous pyelography, which involves injecting dye into your arm vein and taking X-rays as the dye travels through your kidneys and bladder.
• Analysis of passed stones. You may be asked to urinate through a strainer to catch stones that you pass. Lab analysis will reveal the makeup of your kidney stones. Your doctor uses this information to determine what's causing your kidney stones and to form a plan to prevent more kidney stones.
Treatments and drugs
Treatment for kidney stones varies, depending on the type of stone and the cause.Small stones with minimal symptoms
Most kidney stones won't require invasive treatment. You may be able to pass a small stone by:• Drinking water.
• Pain relievers. Passing a small stone can cause some discomfort. To relieve mild pain, your doctor may recommend pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others), acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve).
• Medical therapy. Your doctor may give you a medication to help pass your kidney stone.



